AOP
Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)
관점 지향 프로그래밍
왜 필요한가?
😕예를 들어,
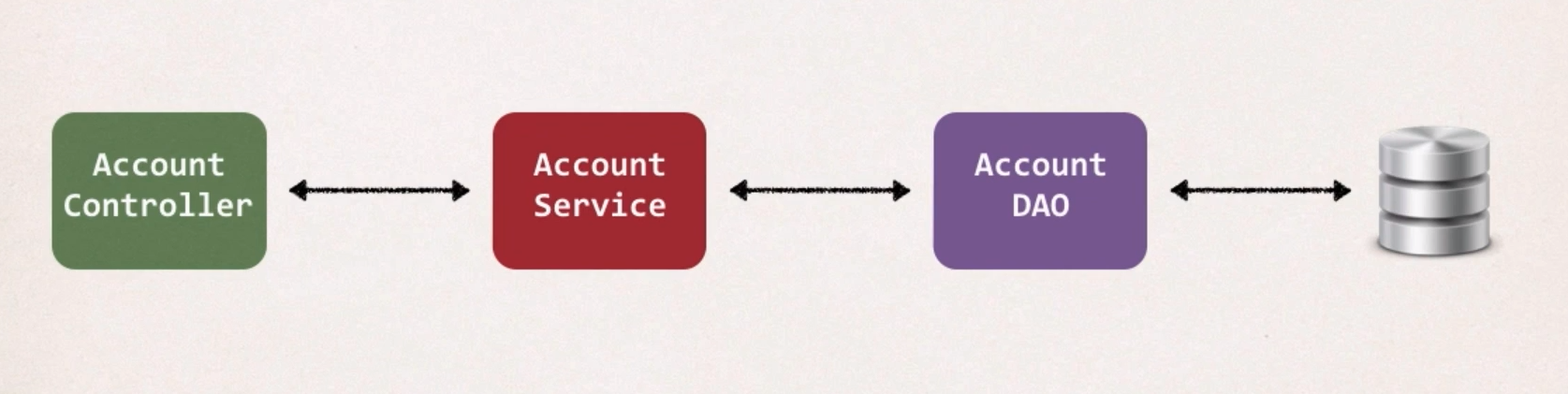
우리의 프로그램 구조가 다음과 같을 때, 몇 가지 요구사항을 받게 되었다.
Our Application Architecture
Code for Data Access Object (DAO)
public void addAccount(Account theAccount, String userId) {
Session currentSession = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
currentSession.save(theAccount);
}
요구사항 1 - Logging
DAO method 실행 전에 로그를 남겨라!
- Need to add logging to our DAO methods
- add some logging statements before the start of the method
Add Logging Code
public void addAccount(Account theAccount, String userId) {
// add code for logging
Session currentSession = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
currentSession.save(theAccount);
}
요구사항 2 - Security
DAO method 실행 전에 보안 인증 작업을 추가해라!
- Need to add security code to out DAO
- Make sure user is authorized before running DAO method
Add Security Code
public void addAccount(Account theAccount, String userId) {
// add code for logging
// add code for security check
Session currentSession = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
currentSession.save(theAccount);
}
요구사항 3 - 모든 layer에 Logging, Security 추가…😑
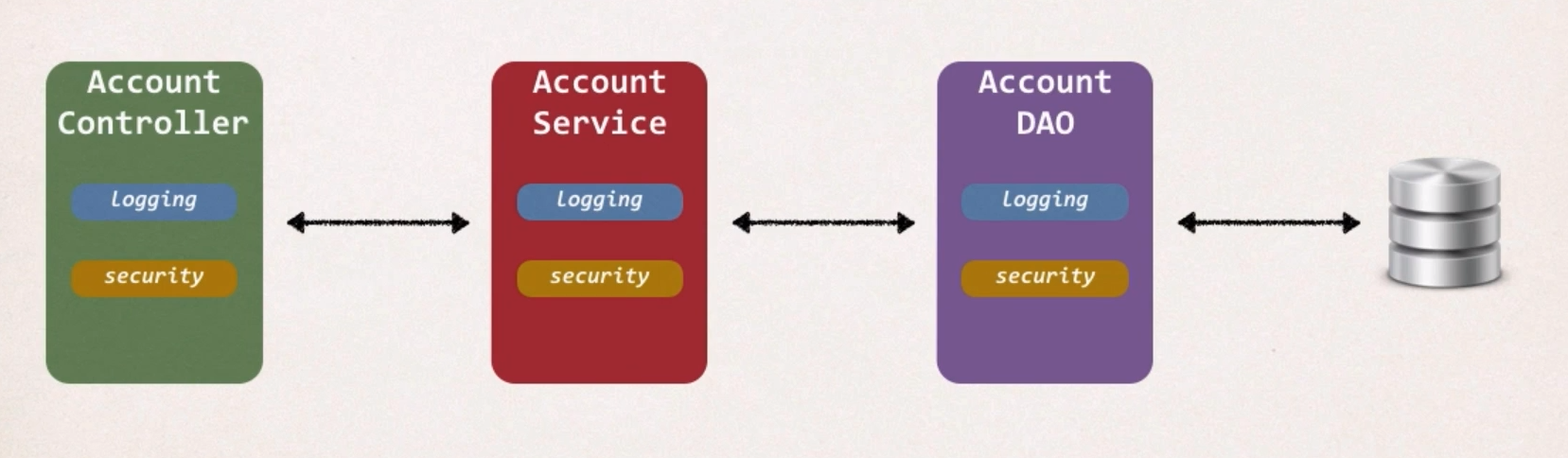
Two Main Problems
- Code Tangling 복잡한 코드
- For a given method :
addAccount(...) - We have logging and security code tangled in
- 즉,
addAccount()는 여러개의 일을 하게 된다. - 핵심 로직의 모듈화 불가능
- For a given method :
- Code Scattering 분산된 코드
- If we need to change logging or security code
- We have to update ALL classes
- 즉, 유지보수가 어려워진다.
가능하지만 여전히 문제가 존재하는 Solutions
- Inheritance 상속 (is a)
- Every class would need to inherit from a base class
- Can all classes extends from your base class? … plus no multiple inheritance
- 즉, 다중 상속도 안되는데, 모든 클래스가 어떤 base class를 상속받을 순 없다.
- Delegation 위임 (has a)
- Classes would delegate logging, security calls
- Still would need to update classes if we wanted to
- add/remove logging or security
- add new feature like auditing, API management, instrumentation
- 모든 클래스에서 logging, security 인스턴스를 가지고 있게 되며, 결국 모든 클래스에 영향도가 있어서 유지보수가 어렵다.
😆답은 AOP !!
공통 관심 사항을 캡슐화하자.
- Programming technique based on concept of an Aspect
- Aspect encapsulates cross-cutting logic : Cross-Cutting Concerns (공통관심사항)
Terms
- Aspect : module of code for a cross-cutting concern (logging, security)
- Advice : what action is taken and when it should be applied
- Join Point : when to apply code during program execution
- Pointcut : a predicate expression for where advice should be applied
- Weaving : Connecting aspects to target objects to create an advised object
💛Aspect
공통관심사항을 모듈화 한 것
- Aspect can be reused at multiple locations
- applied based on Configuration
💛Advice
실행될 로직
- Advice Types
- Before advice : run before the method
- After (finally) advice : 항상 실행 run after the method (finally)
- After returning advice : 성공하면 실행 run after the method (success execution)
- After throwing advice : 실패하면 실행 run after method (if exception thrown)
- Around advice : run before and after method
💛Join Point
Aspect 객체에서 작성한 코드(Advice)가 실행될 시점 (when)
- exception-level : 예외(exception)가 발생되는 시점
- field-level : 필드(field)가 수정되는 시점
- constructor-level : 객체가 생성(constructor)되는 시점
- method-level : 특정 메소드가 호출되는 시점
💛Pointcut
Aspect 객체에서 작성한 코드(Advice)가 실행될 지점 (where)
- PointCut Designator (PCD)
executionwithinargsthistarget@target@args@within@annotation
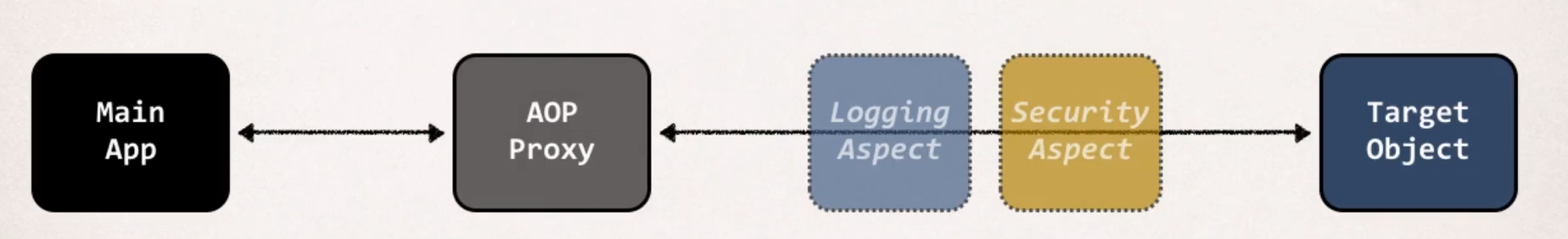
💛Weaving
Aspect 클래스에 정의한 Advice 로직을 Target 에 적용하는 것
즉, 공통코드(advice)를 핵심 로직 코드에 삽입하는 것
- Different types of weaving
- compile-time
- load-time
- run-time (가장 느림)
AOP Frameworks for Java
👉AspectJ
- Original AOP framework, released in 2001
- Provides complete support for AOP
- Rich support for
- join points : method-level, constructor-level, field-level
- code weaving : compile-time, post compile-time, load-time
👉Spring AOP
- Spring provides AOP support
- Key component of Spring
- Security, transactions, caching etc
- Uses run-time weaving of aspects
- only method-level
- 그리고, AspectJ jar 가 필요하다
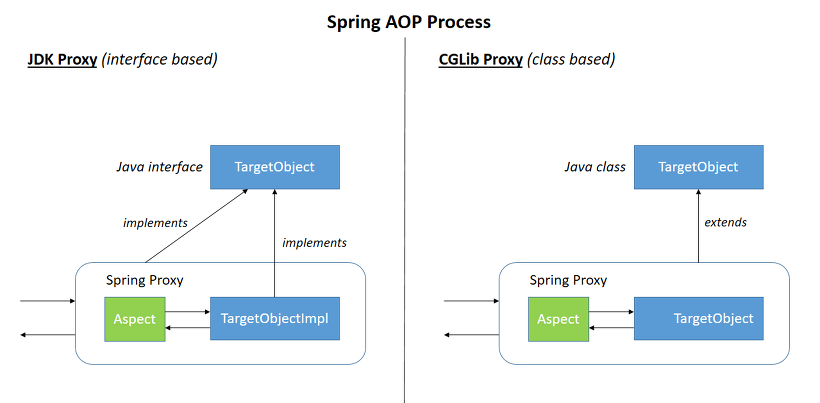
Proxy design pattern
- AOP proxy : an object created by the AOP framework in order to implement the aspect contracts (advise method executions and so on). In the Spring Framework, an AOP proxy will be a JDK dynamic proxy or a CGLIB proxy.
- 요샌 거의 CGLIB proxy만 쓰는 것 같다고 함
🧐Spring AOP vs AspectJ
| Spring AOP | AspectJ | |
|---|---|---|
| pointcut syntax | simple | complex |
| join point | only method-level | all |
| weaving | run-time | compile-time / post compile-time / load-time |
| performance | slower | faster |
| dependency | need AspectJ jar (migration) | . |
| work with | Beans Created by application context | any POJO |
| design pattern | proxy pattern | . |
Test Example
1.create target object
@Component
public class AccountDAO() {
public void addAccount() {
System.out.println(">> DB Work :: insert account data");
}
}
2.create spring java config class
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //AspectJ 를 이용해서 Spring AOP 를 사용하여백그라운드에서 Proxy 사용
@ComponentScan("com.example.aop")
public class ExConfig {
}
3.create main app
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ExConfig.class);
AccountDAO dao = context.getBean("accountDAO", AccountDAO.class);
dao.addAccount();
context.close();
}
}
4.create an aspect with @Before advice
@Aspect //org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect
@Component
public class MyLoggingAspect { //aspect
//advice
@Before("execution(public void addAccount())") //pointcut
public void beforeAddAccountAdvice() {
System.out.println("I'm @Before advice !!!")
}
}
5.result
I'm @Before advice !!!
>> DB Work :: insert account data
✅Benefits of AOP
- Code for Aspect is defined in a single class
코드가 중복/분산되지 않는다. (Not scattered)
- Much better than being scattered everywhere
- Promotes code reuse and easier to change
- Business code in your application is cleaner
핵심 로직을 깔끔하게 작성할 수 있다. (Not Tangled)
- Only applies to business functionality :
addAccount - Reduces code complexity
- Only applies to business functionality :
- Configurable
MainApp 코드를 변경할 필요없이, Configuration 으로 선택적 적용 가능
- Based on configuration, apply Aspects selectively to different parts of app
- No need to make changes to main application code … very important!
✅Advantages
- 재사용성 증가 : Reusable modules
- tangling/scatter 해결 : Resolve code tangling/scatter
- 선택적 적용 : applied selectively based on configuration
✅Disadvantages
- 디버깅 어려움 : too many aspects and app flow » hard to flow
- 비용 증가 : minior performance cost for aspect execution (run-time weaving)
✅Use Cases
- Most common
- logging, security, transactions
- Audit logging
- who, what, when, where
- Exception handling
- log exception and notify DevOps team via SMS/email
- API Management
- how many times has a method been called user
- analytics : peak times, average load, top user
Reference
- Udemy
- Spring 5: Learn Spring 5 Core, AOP, Spring MVC, Spring Security, Spring REST, Spring Boot 2, Thymeleaf, JPA & Hibernate by Chad Darby
- Docs
- Blogs