다익스트라(Dijkstra)
다익스트라(Dijkstra)
그래프에서 DP(Dynamic Programming)를 활용한 최단 경로 탐색 알고리즘(Shortest Path Algorithm).
특정한 하나의 정점에서 다른 모든 정점으로 가는 최단 경로를 구할 수 있다.
가중치가 음수인 간선이 존재한다면 결과가 보장되지 않는다.
하지만, 또 다른 최단 경로 탐색 알고리즘 중 하나인 벨만-포드 알고리즘 보다 시간복잡도 O(Nlog N)으로 더 빠르다.
큰 문제를 작은 문제로 나누어 접근하는 DP의 방식처럼
다익스트라 알고리즘에서 구하고자하는 최단 경로의 부분경로도 최단 거리로 이루어져있다.
예시
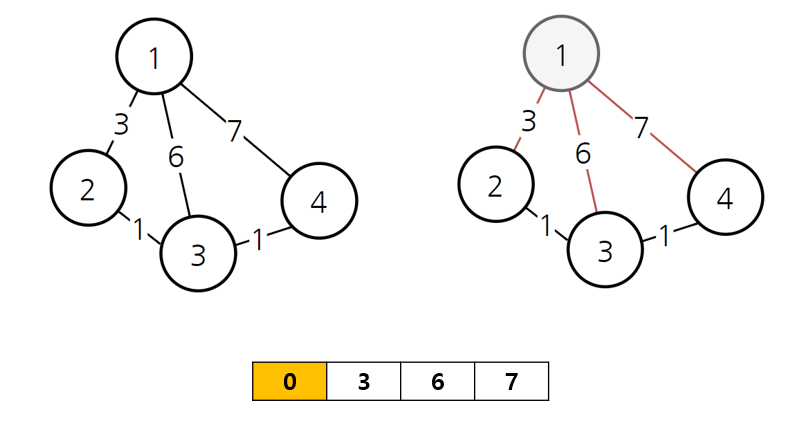
아래 그래프에서 1번 정점에서 출발하여 다른 모든 정점에 도착하는 최단 경로를 구하고자 한다.
1번 정점에서 갈 수 있는 정점과 그 비용은 다음과 같다.
1번 정점에서 탐색했을 때, 1번 정점에서 갈 수 있는 다른 정점들까지의 비용을 최단 거리 배열에 저장한다.
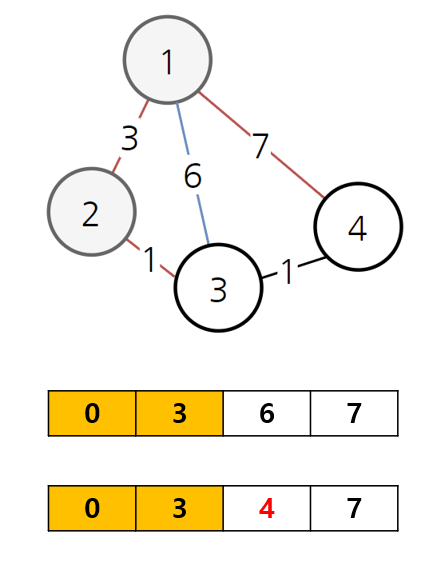
탐색하지 않은 정점 중 가장 비용이 작은 정점은 2번 정점이다.
1번 정점에서 2번 정점으로 가는 최단 경로는 1-2, 최소 비용은 3이 된다.
2번 정점에서 갈 수 있는 다른 정점까지의 비용을 탐색한다.
1번 정점에서 3번 정점을 가기 위해 1-3 경로를 6의 비용으로 가는 것보다 1-2-3 경로를 (3+1)의 비용으로 가는 것이 더 저렴하기 때문에,
최단 거리 배열을 업데이트 해준다.
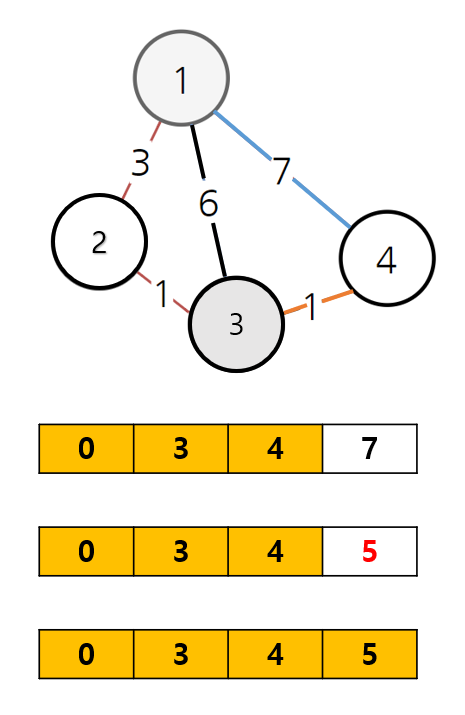
탐색하지 않은 정점 중 가장 비용이 작은 정점은 3번 정점이다.
이제, 1번 정점에서 3번 정점으로 가는 최단 경로는 1-2-3, 최소비용은 4가 된다.
3번 정점에서 갈 수 있는 다른 정점까지의 비용을 탐색한다.
1번 정점에서 4번 정점을 가기위해 1-4 경로를 7의 비용으로 가는 것보다 1-2-3-4 경로를 (3+1+1)의 비용으로 가는 것이 더 저렴하기 때문에,
최단 거리 배열을 업데이트 해준다.
탐색하지 않은 정점은 마지막으로 4번 정점 하나 남았다.
하지만 4번 정점만 남아있기까지 모든 정점들의 최단 경로를 구했기 때문에 더이상 최단 거리 배열은 업데이트되지 않는다.
Solve Problem
백준 18223 민준이와 마산 그리고 건우
첫 번째 풀이
민준이가 마산까지 가는 최단 경로에 건우가 있을 수 있다면,
(a) 건우->민준 최단 경로의 가중치 합
(b) 건우->마산 최단 경로의 가중치 합
(c) 민준->마산 최단 경로의 가중치 합
(a) + (b) = (c) 가 될 수 밖에 없다고 생각했다.
dijkstra 함수를 (a),(b),(c) 경우마다 호출하여 총 3번 최단 경로를 계산하게 되므로 3배의 시간이 소요된다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main_bj_18223_민준이와마산그리고건우 {
public static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
public static int v,e, GUNWOO;
public static boolean[] visited;
public static ArrayList<int[]>[] adj;
public static int[] pToMinjune, pToMasan, minjuneToMasan;
public static int MINJUNE, MASAN;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
input();
init();
dijkstra(GUNWOO, MINJUNE, pToMinjune);
dijkstra(GUNWOO, MASAN, pToMasan);
dijkstra(MINJUNE, MASAN, minjuneToMasan);
System.out.println(isSavedHim() ? "SAVE HIM" : "GOOD BYE");
}
private static void input() throws IOException {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("solveProblem/res/Main_bj_18223_민준이와마산그리고건우.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
v = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // vertex
e = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // edge
GUNWOO = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 건우는 민준이와 같은 곳에 있거나 마산에 있을 수도 있다.
adj = new ArrayList[v+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
while (e-- > 0) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
adj[a].add(new int[]{b, c});
adj[b].add(new int[]{a, c});
}
br.close();
}
private static void init() {
MINJUNE = 1;
MASAN = v;
pToMinjune = new int[v+1];
pToMasan = new int[v+1];
minjuneToMasan = new int[v+1];
Arrays.fill(pToMinjune,INF);
Arrays.fill(pToMasan,INF);
Arrays.fill(minjuneToMasan,INF);
}
private static void dijkstra(int start, int end, int[] dist) {
visited = new boolean[v + 1];
visited[start] = true;
dist[start] = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((int[] o1, int[] o2) -> (Integer.compare(o1[1], o2[1])));
pq.offer(new int[]{start, dist[start]});
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] node = pq.poll();
int current = node[0];
int d = node[1];
if(current == end) break;
visited[current] = true;
for (int[] nextNode : adj[current]) {
int next = nextNode[0];
int w = nextNode[1];
if(visited[next]) continue;
if (dist[next] > w + d) {
dist[next] = w + d;
pq.offer(new int[]{next, dist[next]});
}
}
}
}
private static boolean isSavedHim() { return pToMinjune[MINJUNE] + pToMasan[MASAN] == minjuneToMasan[MASAN]; }
}
두 번째 풀이
별도로 Node 클래스를 정의하고 해당 노드까지 경로의 가중치 합(weight)과 해당 경로에서 건우를 구했는지 여부(save)를 저장한다.
Node 객체를 Priority Queue에 넣고 weight로 정렬하여 다익스트라 알고리즘으로 최단 경로를 찾을 때 사용하는데,
이 때, 만약 weight가 같으면 save 값이 true인 경우(건우를 구했을 경우) 우선순위를 두어 최단 경로가 여러 개 일 때 건우를 구하는 경로를 먼저 고려할 수 있다. (Node 클래스에서 compareTo 함수 오버라이딩된 부분 참고)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main_bj_18223_민준이와마산그리고건우_2 {
public static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
public static int v,e,p;
public static boolean[] visited;
public static ArrayList<Node>[] adj;
public static int[] dist;
private static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
public int vertex;
public int weight;
public boolean save;
public Node(int vertex, int weight) {
this(vertex, weight, false);
}
public Node(int vertex, int weight, boolean save) {
super();
this.vertex = vertex;
this.weight = weight;
this.save = save;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
if(this.weight > o.weight) return 1;
else if(this.weight < o.weight) return -1;
else {
if(this.save) return -1;
else return 1;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
init();
dijkstra(1, v);
}
private static void init() throws IOException {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("solveProblem/res/Main_bj_18223_민준이와마산그리고건우.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
v = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // vertex
e = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // edge
p = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 건우는 민준이와 같은 곳에 있거나 마산에 있을 수도 있다.
adj = new ArrayList[v+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
while (e-- > 0) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
adj[a].add(new Node(b, c));
adj[b].add(new Node(a, c));
}
dist = new int[v+1];
Arrays.fill(dist,INF);
visited = new boolean[v + 1];
br.close();
}
private static void dijkstra(int start, int end) {
dist[start] = 0;
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new Node(start, dist[start]));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node current = pq.poll();
if(current.vertex == p) current.save = true;
if(current.vertex == end) {
System.out.println(current.save ? "SAVE HIM" : "GOOD BYE");
break;
}
if(visited[current.vertex]) continue;
for (Node next : adj[current.vertex]) pq.offer(new Node(next.vertex, current.weight + next.weight, current.save));
visited[current.vertex] = true;
}
}
}
백준 1261 알고스팟
이게 그래프인가? 하는 생각이 들었던 문제였다.
2차원 배열의 각 좌표를 하나의 정점으로 생각하고 각 좌표사이의 거리를 가중치로 계산하여 다익스트라 알고리즘으로 최단 거리를 구할 수 있다.
첫 번째 풀이
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main_bj_1261_알고스팟 {
private static int[] dx = {1,0,-1,0};
private static int[] dy = {0,1,0,-1};
private static char[][] map;
private static boolean[][] visited;
private static int n,m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("solveProblem/res/Main_bj_1261_알고스팟.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
visited = new boolean[m][n];
map = new char[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
map[i] = br.readLine().toCharArray();
}
System.out.println(bfs(0, 0));
br.close();
}
private static int bfs(int x, int y) {
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((int[] o1, int[] o2)->(Integer.compare(o1[2],o2[2])));
pq.offer(new int[]{x, y, 0});
visited[y][x] = true;
int nx,ny;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] pos = pq.poll();
if(isArrived(pos[0], pos[1])) return pos[2];
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
nx = pos[0] + dx[d];
ny = pos[1] + dy[d];
if (!isRange(nx, ny)) continue;
if(visited[ny][nx]) continue;
visited[ny][nx] = true;
if(map[ny][nx] == '0') pq.offer(new int[]{nx,ny,pos[2]});
else pq.offer(new int[]{nx, ny, pos[2] + 1});
}
}
return 0;
}
private static boolean isArrived(int x, int y) {
return x == (n-1) && y == (m-1);
}
private static boolean isRange(int x, int y) {
return (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m);
}
}
두 번째 풀이
deque를 사용하자 시간이 96ms 까지 줄어들었다.
벽을 안부숴도 되는 경우(map[ny][nx] == '0')를 항상 큐의 맨 앞에 먼저 넣어줄 수 있다는 것을 이해해야한다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main_bj_1261_알고스팟_2 {
private static int[] dx = {1,0,-1,0};
private static int[] dy = {0,1,0,-1};
private static char[][] map;
private static boolean[][] visited;
private static int n,m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("solveProblem/res/Main_bj_1261_알고스팟.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
visited = new boolean[m][n];
map = new char[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
map[i] = br.readLine().toCharArray();
}
System.out.println(bfs(0, 0));
br.close();
}
private static int bfs(int x, int y) {
Deque<int[]> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
dq.offer(new int[]{x, y, 0});
visited[y][x] = true;
int nx,ny;
while (!dq.isEmpty()) {
int[] pos = dq.poll();
if(isArrived(pos[0], pos[1])) return pos[2];
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
nx = pos[0] + dx[d];
ny = pos[1] + dy[d];
if (!isRange(nx, ny)) continue;
if(visited[ny][nx]) continue;
visited[ny][nx] = true;
if(map[ny][nx] == '0') dq.offerFirst(new int[]{nx,ny,pos[2]});
else dq.offerLast(new int[]{nx, ny, pos[2] + 1});
}
}
return 0;
}
private static boolean isArrived(int x, int y) {
return x == (n-1) && y == (m-1);
}
private static boolean isRange(int x, int y) {
return (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m);
}
}
Reference https://m.blog.naver.com/ndb796/221234424646